Acronym vs Abbreviation: What’s the Difference Between Them?
Acronyms and abbreviations are not the same—and understanding the difference is essential for precise communication. Whether you are writing an academic paper, preparing a professional report, or communicating online, correctly distinguishing between acronyms, abbreviations, and initialisms improves clarity and reduces ambiguity. For students and researchers, platforms such as Scifocus support academic reading and writing workflows, helping users stay consistent with terminology while drafting or revising scholarly content.
What is an abbreviation?
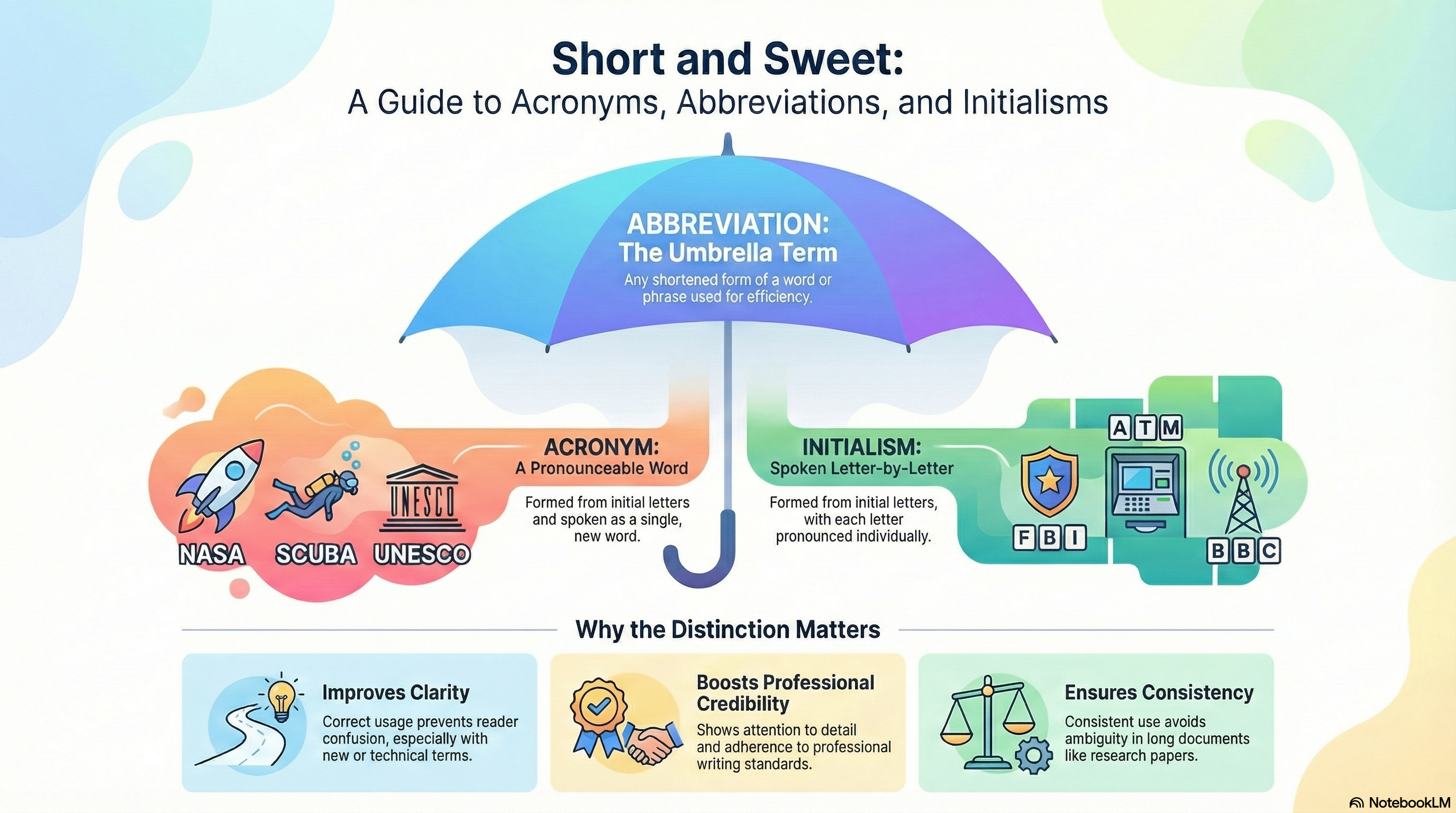
An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase used to save space and improve efficiency without changing the original meaning. Common examples include “Dr.” for “Doctor,” “etc.” for “et cetera,” and “Inc.” for “Incorporated.” Abbreviations appear across academic writing, business communication, and everyday language.
What makes abbreviations interesting is how invisible they have become. Most people use them automatically. Take “USA,” for instance. It is an abbreviation of “United States of America,” yet its familiarity makes it feel like a complete expression rather than a shortened form. For formal definitions and usage standards, authoritative sources such as the Cambridge Dictionary and Merriam-Webster remain essential references.
In academic contexts, abbreviations often extend beyond simple word shortening. Technical writing frequently relies on standardized forms like “mmHg” for millimeters of mercury or “Fig.” for figures. During drafting and revision, academic writing tools highlighted on the Scifocus product feature page can assist writers in maintaining consistent abbreviation usage across longer documents.
What is an acronym?
An acronym is a specific type of abbreviation formed from the initial letters of a phrase and pronounced as a single word. Familiar examples include NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration), UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization), and SCUBA (Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus).
Acronyms are especially common in scientific, governmental, and technical fields, where lengthy names or recurring terms can interrupt readability. Everyday language also adopts acronyms, such as LOL (“laugh out loud”) or YOLO (“you only live once”), illustrating how these forms move easily between formal and informal contexts.
In academic writing, acronyms are typically introduced by spelling out the full term at first mention, followed by the acronym in parentheses. Managing this consistency across multiple drafts can be challenging. Tools within the Scifocus Daily Academic Toolkit are designed to support structured academic writing and help writers keep terminology consistent throughout a manuscript.
How does an initialism differ from an acronym?
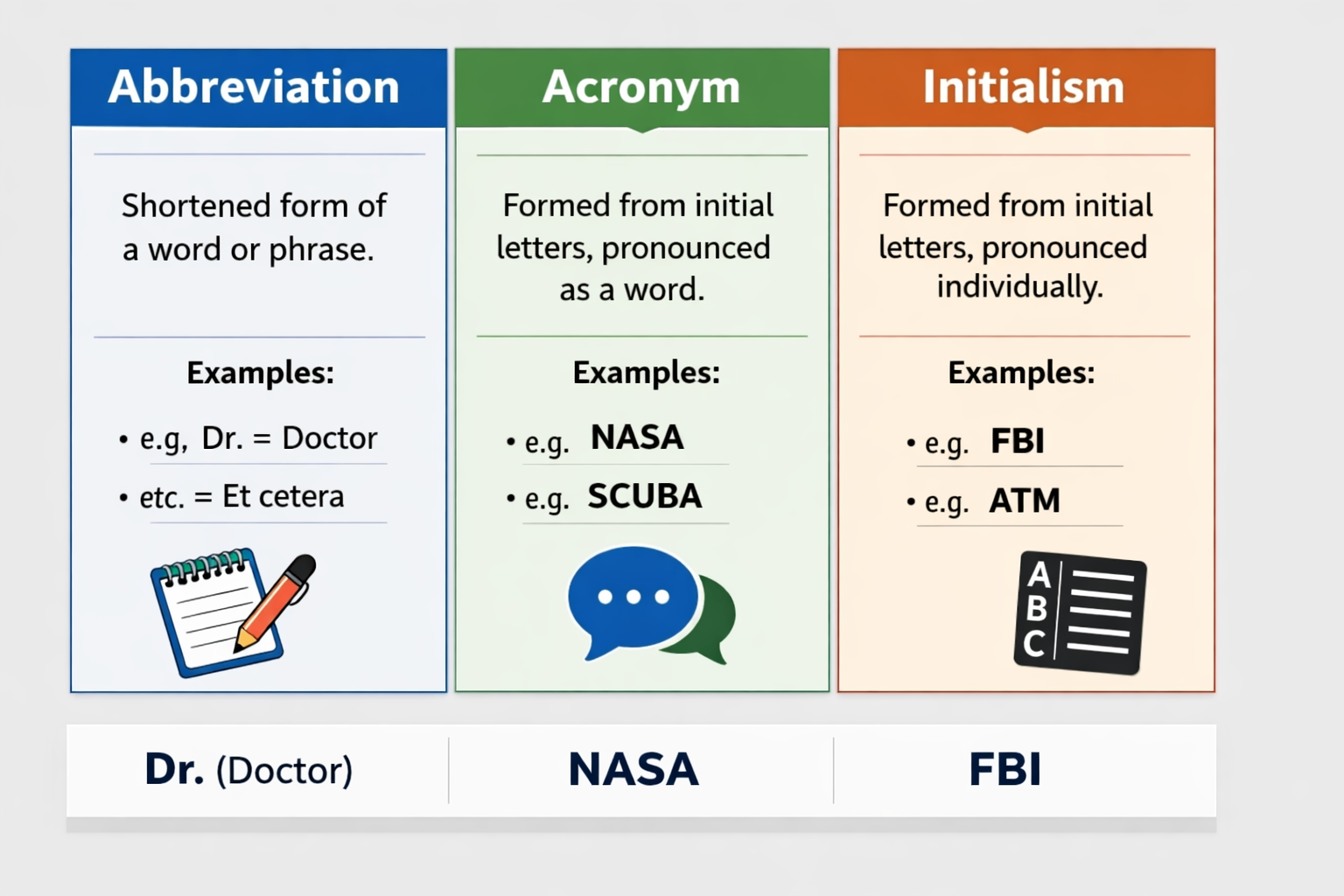
An initialism is formed from the initial letters of a phrase but is pronounced letter by letter rather than as a word. Examples include FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation), ATM (Automated Teller Machine), and BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation).
Although the distinction may seem subtle, it affects readability and tone. Acronyms like NASA flow naturally in sentences, while initialisms require readers to process each letter individually. In formal academic and professional writing, these differences influence clarity and reader engagement.
Over time, some initialisms evolve into commonly spoken words. “Radar” (RAdio Detection And Ranging) began as an acronym but is now treated as an ordinary noun. When organizing terminology within longer research documents, writers using Scifocus Research Assistant Pro can focus on structure and coherence rather than manually tracking terminology usage.
Why is the distinction important?
Distinguishing between abbreviations, acronyms, and initialisms matters for several reasons:
- Clarity in communication: Incorrect usage can confuse readers, especially when introducing new or technical terms.
- Professional credibility: Precise language reflects attention to detail and academic rigor.
- Consistency in writing: Scholarly texts rely on uniform terminology to avoid ambiguity.
Even small inaccuracies can undermine the perceived quality of academic work. Platforms like Scifocus are positioned to support the writing process itself, not to replace dictionaries or editorial standards.
Are there regional or contextual differences?
Yes. Usage conventions often vary by region, discipline, and publication guidelines.
- USA vs US: Both abbreviate “United States,” but “USA” is more common in formal titles, while “US” is frequently used within running text.
- Discipline-specific norms: Academic journals often define strict rules for abbreviation and acronym usage.
While journal style guides remain authoritative, drafting tools referenced on the Scifocus product feature page can assist writers during revision and formatting stages.
How can one determine the appropriate usage?
When choosing between abbreviations, acronyms, or initialisms, consider:
- Audience familiarity: Less familiar terms should be spelled out initially.
- Context: Academic and technical writing prioritizes precision.
- Frequency: Repeated terms often benefit from standardized shortening.
For example, “PCR” (polymerase chain reaction) is widely recognized in biology but is still commonly defined at first mention. Using structured writing tools such as Scifocus DAT helps maintain consistency across longer academic drafts.
What are some practical examples?
- Abbreviations: Dr., etc., Inc., USA
- Acronyms: NASA, SCUBA, UNESCO, LOL
- Initialisms: FBI, ATM, BBC, DNA
These examples highlight differences in pronunciation, tone, and reader perception.
Are there special cases to consider?
Some shortened forms do not fit neatly into standard categories:
- Mnemonics: ROYGBIV for the colors of the rainbow
- Acrostics: Educational or memory-based letter arrangements
- Hybrid forms: Words like “radar” and “laser,” which originated as acronyms and evolved into common nouns
Authoritative references such as Oxford Dictionaries remain useful for clarification.
How do acronyms and abbreviations evolve?
Language is dynamic. Many terms created for technical accuracy eventually enter everyday usage, sometimes losing their original capitalization or perceived abbreviation status. Monitoring these shifts is an important part of academic writing and revision.
FAQs
What is the difference between an acronym and an abbreviation?
An acronym forms a pronounceable word from initial letters, while an abbreviation broadly refers to any shortened form.
Is “USA” an acronym or an abbreviation?
It functions as both: it shortens “United States of America” and is commonly pronounced as a word.
Are all acronyms abbreviations?
Yes, but not all abbreviations are acronyms.
How do initialisms differ from acronyms?
Initialisms are pronounced letter by letter, whereas acronyms are read as words.
How should researchers manage acronyms and abbreviations in writing?
They should define terms clearly on first use, follow journal guidelines, and maintain consistency. Structured writing support tools such as Scifocus RAP can assist with document organization.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between acronyms, abbreviations, and initialisms is essential for clear and professional academic communication.
For writers seeking structured support during drafting and revision, Scifocus provides academic writing tools, including the Daily Academic Toolkit and Research Assistant Pro. New users may explore available features through the free trial.
Did you like this article? Explore a few more related posts.
Start Your Research Journey With Scifocus Today
Create your free Scifocus account today and take your research to the next level. Experience the difference firsthand—your journey to academic excellence starts here.
